Wastewater now and in the future is a challenge that needs to be addressed with a long term approach. Wastewater treatment has emerged as a frontrunner, with the capability to address existing water demand-supply gap to a large extent. It plays an instrumental role in reducing the dependency on the current depleting ground water resource in the country.
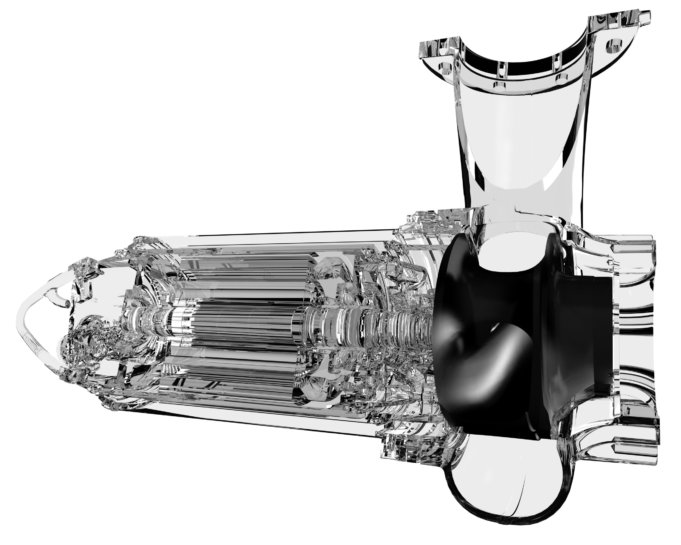
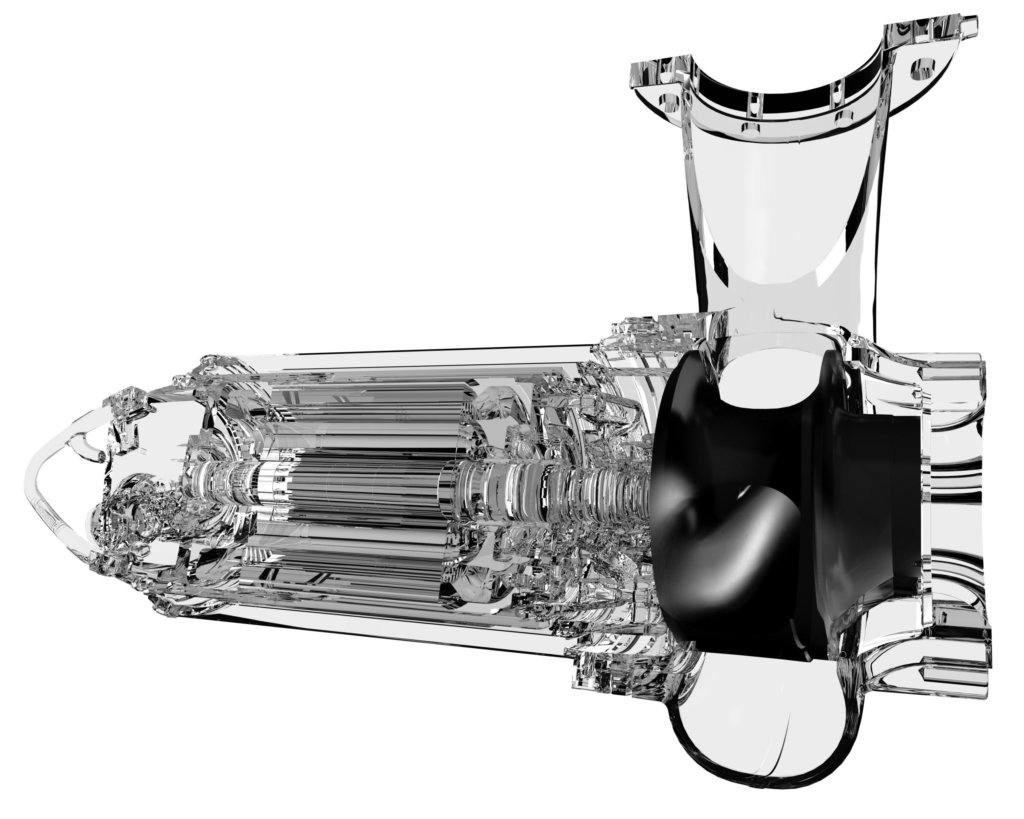
The rising price of fresh water plus a range of new environmental factor and most importantly the energy cost of transporting wastewater to the treatment plant must be accounted for when planning a modern wastewater system. Grundfos India, a global leader in advanced water solutions and a trendsetter in water technology has introduced its innovate SE1 pump with an S-tube impeller to cater in the wastewater treatment processes. The Grundfos S‐tube impeller is designed to help to meet all these diverse challenges.
The challenges facing modern utilities
The main and interlinked challenges which the water utility companies face today in relation to the transport of wastewater are:
- Rising cost of water and energyand stricter government controls
- Lower water consumption and energy usage
- Less fluid mix of modern wastewater
Aside from stricter controls on usage, the rising cost of energy has increased the incentive to find more efficient methods of transporting wastewater. Water‐saving innovations have also created new problems. For example, more efficient toilets use less transportation fluid, thus increasing the risk of clogging farther down the line. Traditional wastewater pumps add to this clogging risk rather than solve it because of the design issues such as, leading edges on which waste material easily gets caught, bends in the pipework, cutting mechanisms and reduced free passages.
What makes S-tube impeller a unique proposition
The fundamentals of the revolutionary S‐tube impeller, have actually been on pump designers’ drawing boards for decades. The volume and diversity of waste material to be transported was relatively low, and therefore details such as the water and energy usage were barely considered by utility providers. It is only in the past two decades that a variety of factors have all collided to make the S‐tube design relevant. These include: increased environmental awareness, newgovernment legislation and directives, and the rising cost of water, energy and wastewater transport.
- Modern wastewater management systems must be able to transport an increased volume and diversity of waste over longer distances, but using less energy and transportation fluid
- This requires a centrifugal pump that does not compromise on either clogging or hydraulic efficiency and offers extended life span with minimal maintenance
- Special features at the front and back plate of the closed S‐tube also optimises the leak flow into the cavities between the rotating impeller and the stationary pump housing
- Because the non‐compromised inner diameter of the S‐tube is uniform, there is less likelihood of clogging, even with a relatively low volume of transportation fluid as found in modern‐day wastewater
- Consequent hydraulic efficiency gains drive down energy costs for the end‐user
- Furthermore the lack of a leading edge has the benefit of significantly lowering NPSH inside the centrifugal pump where the hydraulic system is most prone to cavitation
Integrated with motors, hydraulics and a seamless functionality, the intelligent SE1 solutions is one of the most efficient wastewater pumps. Grundfos SE range of pumps with an S-tube impeller have also been able to significantly boost energy savings in wastewater operations while simultaneously reducing the number of jamming related incidents.
Applications
- This cutting-edge solution is ideal for processes with a higher volume of water/liquid flow
- They areused to handle wastewater, process water and unscreened water processes in municipalities, utility and industrial applications