Photo: www.bsil.com

Global Delivery Head
Blue Star Infotech Ltd.
The IT sector will play a crucial role in enhancing the vision of making India a manufacturing hub. As more and more advances in technology create opportunities for manufacturing to adopt and integrate IT with its processes, one can envision a stronger, sustainable and innovative trend sweeping the manufacturing sector, notes Ramesh Subramanian, Global Delivery Head, Blue Star Infotech Ltd.
Can the Indian manufacturing sector really contribute 25 per cent to GDP and create 100 million new jobs till 2020? Can the vision of making India a manufacturing hub be realised? The answer to such questions is a resounding Yes! How one may ask? As the focus of policy making has now shifted back to the manufacturing sector, IT/ITeS will play a vital role in raising this sector’s significance in the economy.
The role of information technology has transformed from simple automation to driving efficiencies to driving revenue streams. Many manufacturing units have already incorporated several IT tools in their operations. International Data Corporation predicts that by FY16, the business opportunity in the manufacturing domain will be valued at $68 billion in IT services. The outreach IT has been boundless and industries across verticals have benefited in terms of revenue as well as quality with the integration and incorporation of IT or IT services in its systems.
However Indian manufacturing still lags behind in adoption of ICT in core processes. While some industries like automobile and chemicals have seen good progress and are at par with their global peers, the challenges lie particularly with small manufacturers, SMEs and MSMEs. IT deployment may be seen in certain functions like finance and accounts, and HR; however, critical and complicated IT systems like supply chain management, inventory management or enterprise resourcing planning or overall integration of IT into every business process to improve productivity and efficiency is still low.
Digital manufacturing
Digital manufacturing is the amalgamation of computer-based system comprising simulation, visualisation, analytics and collaboration tools to create product and manufacturing process definitions. It is an end-to-end process from designing a product to virtually simulating it. Currently, companies incorporate computer aided tools to design and then graduate to creating product prototypes and then after finalising on prototypes, they proceed to actual manufacturing. This technique is flawed since inconsistency in design causes a deviation between prototypes and the manufactured product thus resulting in enormous losses. Digital simulations eliminate such errors and thereby reduce corresponding losses.
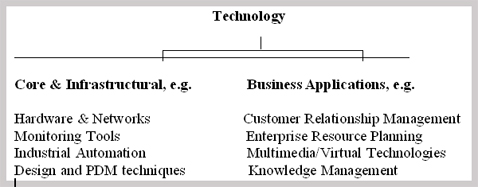
Currently, the use of IT in manufacturing is categorised in two broad categories:
Manufacturers must pay attention while incorporating Disruptive technology to their processes. If well adopted, can enable manufacturers to enhance operational efficiency as well as become more responsive. For instance, the adoption of BI/ Analytics helps a variety of manufacturing and non-manufacturing operations spot trends early and pinpoint areas for improvement. Use of mobile devices and leveraging mobile platforms is also seen as a very prevalent trend among manufacturers. Other technologies waiting in the wings would include additive manufacturing, immersive or augmented reality platforms, wearable’s, etc. which should all be assessed for their applicability to individual business challenges.
Benefits of incorporating IT
Technology offers manufacturing a plethora of advantages ranging from reducing costs to increasing productivity output per employee.
* Significant cuts in production costs: Technology has helped to streamline the production process by eliminating costly waste. Implementing a “lean” manufacturing process like Six Sigma ensures meeting customer demand quickly and efficiently. With the use of automation, the dependence on human beings to perform some of the necessary production processes has reduced. As a result, employee expenses have also reduced.
* Simplicity, homogeneity and flexibility in operations: Technology enables manufacturers to process data on real time basis thus ensuring quick results and actions. Technology also aids in standardisation in selling and in the areas of merchandising.
* Increasing the efficacy of value chain: The entire value chain is automated on an ERP system that reduces costs and improves efficiency and productivity. This adds agility and flexibility to the whole process of value chain. This has already begun happening in India, especially in the larger companies
Challenges of integrating IT
Managing vast, complex data efficiently: Manufacturers and their businesses generate a lot of data such as website analytics, production workflows, sales numbers, financial reports and prospect research, and all of it important and constantly changing. IT tools must effectively record such information that helps manufacturers to monitor deviations and execute corrective measures
High upgradation and maintenance costs: Technology is dynamic and the cost of upgrading technology is also high. Applications that are essential to power day-to-day operations functions such as customer relationship management, data storage, inventory and other technologies supporting shop floor activities need to upgraded in order to sustain efficiency.
Data loss: According to an independent research, 70 per cent organisations experience some form of data loss and hence have to set aside budgets to spend on data storage, backup and protection.
Privacy and cyber security: The exponential growth in structured and unstructured data is sometimes a roadblock for educating both employees and workforce about how productivity can be improved and security breaches can be reduced.
Lack of coordination for seamless integration: It is a challenge to upgrade existing legacy systems and align them with new technologies. The systems developer has to ensure that in this process, previous data is secure and processes correctly respond to new technology in place. This is a time consuming and expensive task.
Lack of skilled manpower: Manufacturing usually lacks skilled workforce who understand the usage of IT and can operate them. There is lack of structured training or vocational training or training to develop IT skills for workers in manufacturing sector. Also, top management lacks the vision on how an empowered workforce can lead to better productivity.
Trends and developments
Some of the trends in technology that can be game-changers for the manufacturing sector are given below:
* Manufacturers employing 3D value chains.
* Investments to modernise existing supply chain technology by focusing on operational resiliency.
* Significant investment to enhance Plant floor IT systems.
* Many manufacturers are trying to reduce their carbon footprint as well as energy use and overall environmental impact. Technology will help such manufacturers to develop sustainable manufacturing initiatives that produce high-quality, cost-effective products and conserve available resources.
The IT sector will play a crucial role in enhancing the vision of making India a manufacturing hub. As more and more advances in technology create opportunities for the manufacturing to adopt and integrate IT with its processes, one can envision a stronger, sustainable and innovative trend sweeping the manufacturing sector.