The Indian economy is growing at a rapid pace creating high demand for raw materials by steel, cement and power plants. It is necessary to improve utilisation of railstock and railway network, the main source of transport of bulk materials, by introducing high-capacity twin tipplers in India, write Yashwant Sakhardande, Senior Vice President, Design and Engineering, and Rajesh Badhe, Deputy General Manager, ThyssenKrupp Industries India Pvt. Ltd, Pune.
Countries with high rate of economic growth like China, Brazil, and Russia are constantly upgrading their port infrastructure to meet increasing demand for import and export of various bulk materials. Twin Wagon Tipplers have been employed extensively to achieve higher unloading rates and improving the utilisation of existing railway infrastructure. In China, at Huanghua coal export terminal, six twin rotary tipplers have been installed to achieve export of 80 million tons of coal per year.

Each tippler at this port simultaneously unloads two rail freight box type wagons, each weighing a maximum 98 tons, at a rate of up to 33 cycles per hour, thus unloading an average 4,000 tons of coal per hour with a maximum capacity of 4,500 tons per hour.
In Brazil, at port Porto Sudeste, two twin tipplers are in operation, each handling 2x140T (gross weight) wagons at 40 dumping tips per hour of iron ore.
Similarly, at Ust Luga, largest port in Russia, two twin tipplers are installed to unload coal at the rate of 3,500 tons per hour each.

Indian scenario
In India, as per old RDSO guidelines, tippler capacity was limited to not more than 20 tips per hour. Hence, side discharge tipplers having max 20 tips per hour were popularly used to unload material from railway wagons of 110T gross weight in ports, power plants, steel plants and cement plants.
Rotary tipplers have been less popular in India in the past, as it calls for 4 to 5 metres deeper underground civil construction than side discharge tipplers, thus making civil costs considerable percentage of total project cost for small-scale projects. Energy requirements of side discharge tippler are higher due to lift and shift type operation while unloading the box wagon. They require heavy counterweights to even out the mechanical effort. Rotary tipplers are energy efficient as they rotate the wagon about its centre of gravity. No counterweights are necessary in this case.
Side discharge tippler design is not suitable for more than 27 to 28 tips per hour and also is not amenable to tipple more than one wagon at a time. As per new RDSO guidelines effective from December 1, 2010, number of tips has been increased to more than 25 tips per hour for side discharge and rotary tipplers to achieve higher unloading capacity and more turnaround of rakes per year. New RDSO guidelines also permit use of single and twin wagon tipplers.
The Indian economy is growing at a rapid pace creating high demand for raw materials by steel, cement and power plants. It is necessary to improve utilisation of railstock and railway network as it is the main source of transport of bulk materials. Thus, necessity is felt to introduce high capacity twin tipplers in India.

Steel plants
Today, new steel, power and cement plants are being set up in India and capacity of existing plants are being expanded. In a steel plant we need to unload approximately 3 tons of raw materials like coal, iron ore, dolomite, limestone etc. for producing one ton of steel. Since all above raw materials are transported by railway wagons, twin tippler is an ideal solution to unload rakes at the high rate of more than 3,500 tons per hour making effective use of limited railstock, smaller rail yard area and limited rail lines connecting to main railway network. This is specially a constraint for landlocked steel plants which want to expand the steel production.
For their new 3 million ton steel plant project at Kalinganagar, Odisha, Tata Steel has incorporated two twin and two single C-type rotary tipplers in the scheme to unload 9 million tons raw materials such as coal, iron ore, limestone and dolomite. This will be first installation of twin tipplers in India.

Twin tippler at Tata Steel, Kalinganagar, will unload 2x140T wagons at a time at the rate of 25 tips per hour and will achieve unloading rate of 3,500 tons per hour. The supplied tipplers are designed as per latest RDSO guidelines and can tipple all type of existing box-type wagons and also proposed DFC and feeder route wagons to be introduced in near future for coal and iron ore transportation.
For bulk export terminal, where we have to load ships in the minimum possible time, twin tippler can play pivotal role of unloading trains carrying coal, iron ore etc. at faster rate and make effective use of limited railstock, smaller rail yard area and limited rail lines connecting to main railway network.
Power plants
The recent trend of installing mega and ultra mega power plants has increased daily coal requirement of power plants substantially. Typically, for a 4,000-MW power plant, coal requirement may be up to 40,000 to 45,000 tons per day. To cater to such high requirement again the rotary twin tippler will satisfy the requirement by unloading at the rate of approximately 3,500 to 5,000 tons per hour in 8 to 12 hours. One can get capacity between 10 to 15 million tpa with one rotary C-frame type twin tippler.

Twin tippler installation and operation
The twin rotary tipplers are of two types, namely ‘O’ type and ‘C’ type tipplers.
The ‘C’ type twin tipplers are now more popular because it has C-shaped frame — open at one side which allows side arm charger to travel through the tippler and place loaded wagons on the tippler platform and to push empty wagon out of platform and help to form the empty rake on outhaul side.
The ‘O’ type tipplers are more popular in the countries where railstock is provided with rotary coupling, and it is not necessary to decouple the wagons during tippling. These tipplers can achieve very high tippling cycles up to 45 tips per hour. Wagon placement on ‘O’ type tippler is done using rope driven side arm charger. Rotary couplings on wagons do not require decoupling and higher tips are feasible. However, this advantage can be derived only in rotary tipplers.
The tippler is controlled by PLC system in manual mode and fully automatic mode. The drives for tippler are either variable speed controlled electro-mechanical drives or hydraulic drives. In case of hydraulic drive, hydraulic power pack can be kept away from dusty environment in separate closed pressurized room. Electric panels of VVFD drives are protected from dusty environment by placing them in a separate airconditioned room. Variable speed controlled electric drives are advanced and effectively used with regenerative braking for both tippler and side arm charger — with consequent reduced demand on the power network. This regenerative feature is not available with hydraulic drives.
A typical installation of twin tippler consists of tippler, wagon positioner, side arm charger, wheel grippers, hopper and apron feeders:
- A positioner (or indexer) pulls the loaded rake through a distance of two wagon lengths towards the tippler platform on inhaul side. The two wagons are decoupled and pulled further to wards the tippler platform.
- Wheel grippers installed on the inhaul side engages with the front wheels of the first loaded wagon standing on the inhaul side, ensuring the fixed position of the leading wagon of loaded rake. Wheel grippers are hydraulically actuated and horizontally arranged.
- Another set of wheel grippers installed just before the platform on inhaul side ensures that two wagons are maintained in fixed position, when indexer arm decouples and side arm charger arm couples with the two loaded wagons.
- A side arm charger which pulls the two wagons, on the tippler platform. Simultaneously, SAC pushes the empty wagons standing on the platform (from previous unloading cycle) to the outhaul side.
- Another set of wheel grippers installed on the outhaul side engages with the rear wheels of the last (tailing) empty wagon standing on the outhaul side, ensuring the fixed position of this last wagon of empty rake.
- SAC continue pushing the empty wagons out of platform with controlled speed until they couple with the last empty wagon of empty rake standing on outhaul side. The wheel gripper is now disengaged so that SAC can continue pushing the empty rake through a distance of two wagons and thus continue to form the empty rake on a level track (or max stipulated gradient of 1:1200 as per RDSO guidelines). The last wagon is than gripped and SAC decouples its arm and returns to original position to take charge of next two loaded wagons placed by positioner — and cycle continues.
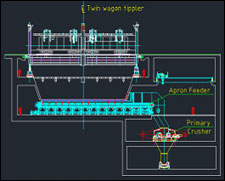
Twin tippler with wheel gripper at inhaul side and outhaul side with wagon positioner and SAC, form a completely automated system for unloading bulk material from wagons and also form empty train at outhaul side. Tippler unloads the material in the hopper. Two apron feeders arranged under the hopper extracts the material at controlled rate and load on the downstream conveyor system. Apron feeders are provided with variable speed hydraulic or electro-mechanical drive.
Many times coal received from mines contain larger number of oversize lumps. If the percentage of oversize material is high, these larger lumps will also be allowed to pass through bigger size grid opening and will be crushed to a desired size by primary crusher located at the discharge end of apron feeder. This enables system to be operated without interruption for clearing the grid and also enables to reduce the lumps to acceptable size suitable for loading on downstream conveyor/system. Refer to Fig.1 showing twin tippler with apron feeder and primary crusher to crush oversize size lumps coming along with the material.
Tandem tippler arrangement
It is also possible to arrange two single wagon rotary tipplers side by side on same rail track. Wagons are placed on the tipplers without decoupling and tippled in synchronised manner. This arrangement can also allow single tippler to be operated when the plant is working at lower capacity or when one tippler is under maintenance. This increases availability of the system; however, investment requirements are higher than twin tippler.
Transfer platform for compact railway yard layout
To form an empty rake at outhaul side, we need around 700m free rail tracks at outhaul. This space at times puts severe constraints in plant layout. Today space is at a premium in plant or at the port and is many times an issue because of shortage of land availability due to cost and environmental issues.
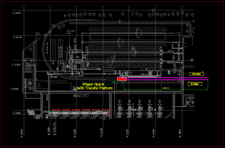
Transfer platform installed after tippler at out haul side is an effective solution to this problem. With the help of transfer platform and built-in puller/pusher, we can transfer empty wagons on a track which is parallel to inhaul track and form the empty train. Thus, around 700m length of track is not required at out haul side. This also avoids circular track in the plant area simplifying the plant layout, eliminating constraints on inplant logistics.
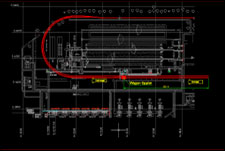
Refer Fig.2 where large plant area is occupied by circular rail track.
In Fig.3, you will find that the complete outhaul circular rail track is eliminated with the help of transfer platform installed at out haul side of twin tippler. This makes the plant layout, internal road and drainage layout much simpler.
Transfer platform can be used in conjunction with side discharge tippler, single/twin and tandem rotary tipplers. Hence, to conclude, rotary C-frame type twin tippler with transfer platform is an ideal choice for steel plant, bulk port terminals and at power plants to unload bulk materials at a faster rate. This avoids demurrage charges and optimises plant rail infrastructure.












Dear Mr. Sakhardande/ Badhe,
Nice to read you on Project Monitor.
Its good article & Knowledge sharing on Wagon Tipplers.
Best Wishes
Vinayak S.Patil.
9764297164